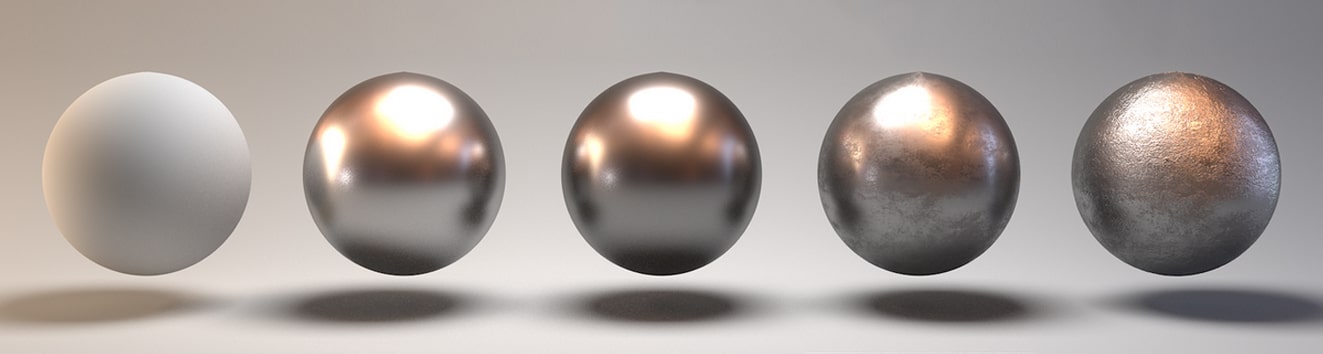
Physically Based Rendering (PBR) has transformed the world of computer graphics and game development by introducing a more accurate and realistic approach to texturing. PBR textures simulate how light interacts with various materials, resulting in stunning 3D visuals that closely resemble their real-world counterparts.
PBR textures are created using either a Metallic or Specular workflow. These workflows define how different properties of a material, such as its reflectivity and roughness, are represented in the texture maps. Understanding the differences between these workflows and knowing how to use PBR textures effectively can greatly enhance the quality and authenticity of your digital creations.
PBR (Physically Based Rendering) textures have revolutionized the world of computer graphics by providing a more realistic representation of materials. When it comes to utilizing PBR Specular Workflow textures, there are two primary workflows: Metallic and Specular.
In the Specular workflow, textures such as Diffuse, Specular, and Glossiness maps are used to control the appearance of the material. The Diffuse map defines the base color, the Specular map controls the intensity and color of reflected light, and the Glossiness map determines the smoothness or roughness of the material's surface.
The Metallic workflow is one of the two primary workflows in PBR (Physically Based Rendering) textures, and it offers a powerful approach to achieving realistic materials. In this workflow, PBR Metallic Workf textures such as Albedo, Metallic, and Roughness maps are utilized. The Albedo map defines the base color of the material, while the Metallic map determines which parts of the material are metallic and which are non-metallic (dielectric).
The Roughness map controls the surface smoothness or roughness of both metallic and dielectric areas. By leveraging the Metallic workflow and properly configuring the PBR Specular Workflow textures, you can create stunning and accurate representations of materials, ranging from shiny metals to rough non-metallic surfaces, in your computer graphics projects.
The Metallic workflow in PBR (Physically Based Rendering) texturing offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for creating realistic materials. One of the key advantages is its simplicity and efficiency. By using the Metallic workflow, you can achieve accurate and visually appealing results with fewer texture maps compared to the Specular workflow. The use of a single Metallic map allows for a clear distinction between metal and non-metal areas, making it easier to create materials with varying degrees of reflectivity. Additionally, the Metallic workflow provides better control over the appearance of metals, allowing for the creation of highly reflective surfaces with a range of roughness values.
The Specular workflow is an important approach in PBR (Physically Based Rendering) texturing that allows for the creation of realistic materials. In this workflow, PBR Specular Workflow textures such as Diffuse, Specular, and Glossiness maps are utilized. The Diffuse map defines the base color of the material, while the Specular map controls the intensity and color of reflected light.
The Glossiness map determines the smoothness or roughness of the material's surface. One of the advantages of the Specular workflow is its flexibility, as it can be used for a wide range of materials, including both metallic and non-metallic substances. It provides fine-grained control over the appearance of materials, allowing for the creation of highly detailed and nuanced surfaces. By leveraging the Specular workflow and properly configuring the PBR textures, you can achieve visually stunning and accurate representations of materials in your computer graphics projects.
The Specular workflow in PBR (Physically Based Rendering) texturing offers several advantages that make it a valuable choice for creating realistic materials. One of the key advantages is its versatility. The Specular workflow can be applied to a wide range of materials, both metallic and non-metallic, allowing for the creation of diverse surfaces such as plastics, ceramics, and fabrics. Another advantage is its flexibility in controlling the reflection properties of materials. The use of separate Diffuse, Specular, and Glossiness maps provides fine-grained control over the material's appearance, allowing for precise adjustments of the color, intensity, and smoothness of the specular highlights.
When it comes to PBR (Physically Based Rendering) texturing, both Metallic and Specular workflows offer distinct advantages. The Metallic workflow excels in creating materials with metallic properties, such as metals and alloys, by utilizing a single Metallic map to define the metalness of the surface. It provides a simpler and more efficient approach with fewer texture maps, making it easier to achieve accurate reflections and varying degrees of roughness. On the other hand, the Specular workflow offers versatility in creating a wide range of materials, including both metallic and non-metallic substances. It allows for precise control over the appearance of specular highlights, color, and smoothness by utilizing separate Diffuse, Specular, and Glossiness maps. The choice between Metallic and Specular workflows depends on the specific requirements of the project and the desired visual outcome.